Vitamins are fundamental to maintaining health and well-being, yet their importance is often overlooked until deficiencies arise. These essential nutrients play a pivotal role in various bodily functions, from supporting the immune system to maintaining healthy skin and vision. Unfortunately, recognizing a deficiency isn’t always straightforward, as symptoms can be subtle and easily mistaken for other health issues. This article delves into the signs and symptoms of being low on key vitamins, offering insights into how to identify and address these deficiencies. Understanding these signs is crucial for taking proactive steps toward better health.
Contents
- 1 Vitamins: Their Essential Roles And Functions
- 2 Vitamin A: Deficiency Signs And Solutions
- 3 B Vitamins: Identifying Deficiencies
- 4 Vitamin C: More Than Just Immune Support
- 5 Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
- 6 Vitamin E: An Essential Antioxidant
- 7 Vitamin K: Crucial For Blood And Bones
- 8 Nourish Your Body, Nourish Your Life
Vitamins: Their Essential Roles And Functions

Vitamins, organic compounds required in small quantities, are crucial for sustaining life and preventing various health disorders. The human body needs these nutrients for growth, digestion, nerve function, and much more. They are categorized mainly into two groups: fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins, including Vitamins A, D, E, and K, are stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver. In contrast, water-soluble vitamins, such as the B-complex vitamins and Vitamin C, need to be replenished more frequently as they are not stored in the body.
Each vitamin plays a unique and irreplaceable role in the body. For instance, Vitamin D is essential for bone health, while Vitamin C is crucial for immune function and skin health. A balanced diet typically provides all the necessary vitamins. However, certain lifestyle factors and health conditions can lead to deficiencies. Recognizing the specific roles of these vitamins is the first step in understanding how their deficiency might manifest in the body.
Vitamin A: Deficiency Signs And Solutions

Vitamin A, vital for maintaining healthy vision, skin, and immune function, can often be deficient in many diets. When the body lacks this essential nutrient, several symptoms may become apparent. These include night blindness, a significant early sign, and more severe issues like xerophthalmia, leading to blindness if untreated. Skin may also become dry and itchy, and there can be an increased susceptibility to infections due to impaired immune function.
Addressing Vitamin A deficiency involves dietary adjustments and, in some cases, supplementation. Rich sources of Vitamin A include liver, fish oils, and a variety of fruits and vegetables like carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens. Beta-carotene, found in these plant sources, is converted by the body into Vitamin A. Ensuring a diet rich in these foods can help restore and maintain adequate Vitamin A levels, thereby preventing the associated health risks.
B Vitamins: Identifying Deficiencies

The B Vitamin complex, encompassing vitamins like B12, B6, and Folate, plays a significant role in energy production, nerve function, and the formation of red blood cells. Deficiencies in these vitamins can lead to a range of symptoms. For instance, a lack of Vitamin B12 or B6 can result in anemia characterized by fatigue and weakness. Neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling in the hands and feet, and even mood changes can also indicate a deficiency in these essential nutrients.
Dietary sources rich in B Vitamins include whole grains, meats, eggs, dairy products, and leafy green vegetables. Vegetarians and vegans, who might not get enough B12 from their diet, may need to consider fortified foods or supplements. Regular consumption of these vitamin-rich foods can help prevent the symptoms associated with their deficiency. Additionally, individuals with certain health conditions or those on specific medications should be particularly mindful of their B Vitamin intake, as they might be at higher risk for deficiency.
Vitamin C: More Than Just Immune Support
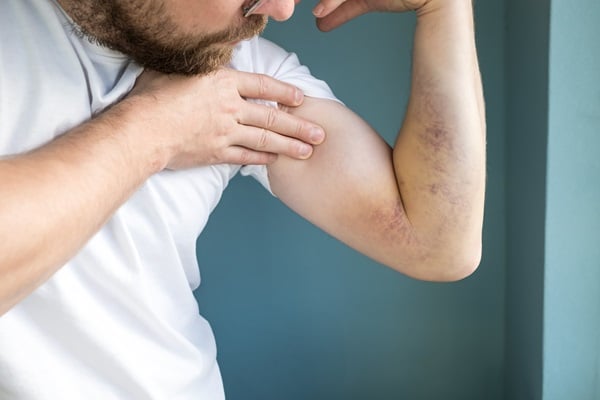
Vitamin C, widely known for its immune-boosting properties, also plays a critical role in collagen synthesis, wound healing, and the maintenance of bones and teeth. A deficiency in this vitamin can lead to a variety of symptoms, some of which are often overlooked. These include easy bruising, bleeding gums, slower wound healing, and, in severe cases, scurvy – a condition once common among sailors. Fatigue, joint pain, and dry, splitting hair are other indicators that the body might be lacking adequate Vitamin C.
To ensure sufficient intake of Vitamin C, incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet is key. Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli are excellent sources. Unlike many animals, humans cannot synthesize Vitamin C and must obtain it from their diet. It’s important to note that Vitamin C is water-soluble and sensitive to heat, so fresh, raw fruits and vegetables are the best sources. For those who struggle to get enough from their diet alone, Vitamin C supplements can be an effective alternative.
Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin

Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is unique because it can be synthesized by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. However, Vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly common, especially in regions with limited sunlight or among individuals with limited sun exposure. Symptoms of deficiency include bone pain, muscle weakness, and, in severe cases, bone malformations such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Mood changes, including symptoms of depression, have also been linked to low levels of Vitamin D.
The primary way to boost Vitamin D levels is through sun exposure, but this needs to be balanced with skin cancer risk. Foods such as fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified dairy, and plant milks can also contribute to the daily intake of Vitamin D. In cases where dietary intake and sunlight exposure are insufficient, supplements may be necessary. It’s important to get your Vitamin D levels checked before starting supplementation, as excessive intake can lead to health complications.
Vitamin E: An Essential Antioxidant

Vitamin E, an essential antioxidant, helps protect cells from oxidative stress, a factor in aging and many chronic diseases. It also plays a role in immune function and skin health. Deficiency in Vitamin E is rare but can occur, particularly in individuals with certain genetic disorders or fat malabsorption issues. Symptoms of Vitamin E deficiency include peripheral neuropathy, muscle weakness, and impaired immune response. In severe cases, it can lead to retinopathy and impaired vision.
Dietary sources of Vitamin E include nuts and seeds, vegetable oils, and green leafy vegetables. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help maintain adequate Vitamin E levels. Since Vitamin E is fat-soluble, it’s best absorbed when consumed with a source of dietary fat. For individuals who cannot get enough Vitamin E from their diet, supplements might be considered, but it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation, as high doses can interfere with certain medications and conditions.
Vitamin K: Crucial For Blood And Bones

Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health. A deficiency in this vitamin can lead to excessive bleeding from wounds or bruising and, in severe cases, hemorrhaging. It can also affect bone health, leading to osteoporosis and increased fracture risk. Vitamin K deficiency is relatively rare but can occur in individuals with certain digestive disorders or those taking certain medications that interfere with vitamin absorption.
The best dietary sources of Vitamin K are green leafy vegetables like kale, spinach, and broccoli, as well as some vegetable oils. For individuals who have difficulty absorbing dietary fat, which is necessary for Vitamin K absorption, supplements may be recommended. As with any supplement, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for those on blood-thinning medications, as Vitamin K can affect their efficacy.
Nourish Your Body, Nourish Your Life
Understanding and addressing vitamin deficiencies is a vital aspect of maintaining overall health. It’s essential to pay attention to the signs your body may be showing and consider dietary adjustments or supplementation as needed. Remember, a balanced diet is key to preventing these deficiencies. If you suspect a deficiency, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and consider getting your vitamin levels checked. Take this knowledge and act now for a healthier, more vibrant you.