Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a pivotal role in bone health, immune function, and overall well-being. Despite its importance, Vitamin D deficiency has become a global concern, affecting individuals across various age groups and geographical locations. Symptoms can be subtle but impactful, ranging from fatigue and bone pain to serious long-term health risks. Understanding the natural ways to combat this deficiency is crucial, as it not only involves sun exposure but also dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes to ensure adequate levels of this essential nutrient.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Vitamin D Deficiency
- 2 The Role of Sunlight in Vitamin D Synthesis
- 3 Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
- 4 Supplements: When and How to Use Them
- 5 Lifestyle Factors Influencing Vitamin D Levels
- 6 The Connection Between Vitamin D and Overall Health
- 7 Monitoring and Maintaining Healthy Vitamin D Levels
- 8 Addressing Challenges and Misconceptions
- 9 Embracing the Sunshine Vitamin for Optimal Health
Understanding Vitamin D Deficiency

Vitamin D deficiency occurs when the body doesn’t absorb enough of this crucial nutrient, leading to a range of health issues, including weakened bones, immune system problems, and an increased risk of chronic diseases. It’s commonly triggered by insufficient sunlight exposure, poor dietary intake, and certain medical conditions. Recognizing the signs of deficiency, such as chronic fatigue, mood changes, and muscle weakness, is vital for timely intervention. Accurate diagnosis often involves blood tests to measure the levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, the most accurate marker of Vitamin D status in the body.
The Role of Sunlight in Vitamin D Synthesis

Sunlight is the most natural and effective way for the body to produce Vitamin D. When the skin is exposed to UVB rays from sunlight, it synthesizes Vitamin D3, the active form of Vitamin D. However, the amount of sunlight needed varies based on factors like skin pigmentation, geographic location, and time of day. It’s crucial to balance sufficient sun exposure with the risk of skin damage; about 10 to 30 minutes of midday sun several times a week is often recommended, depending on individual factors.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
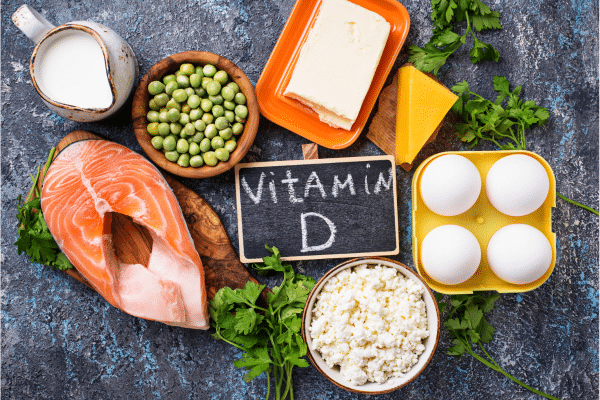

While sunlight is a primary source, certain foods can also boost Vitamin D levels. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in Vitamin D, as are egg yolks and liver. For vegetarians or those with limited sun exposure, fortified foods like dairy products, orange juice, and cereals can be beneficial. Incorporating these Vitamin D-rich foods into daily meals can help mitigate deficiency, especially in regions with less sunlight or for individuals who spend a lot of time indoors.
Supplements: When and How to Use Them
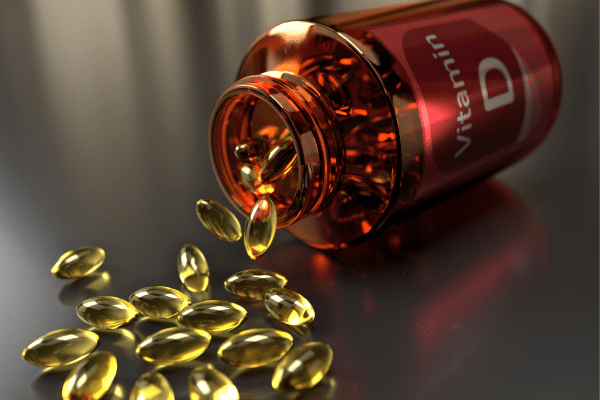

Vitamin D supplements can be a practical solution for those unable to achieve adequate levels through sunlight and diet alone. They are particularly beneficial during the winter months or for individuals with limited sun exposure, darker skin, or specific dietary restrictions. Selecting the right supplement involves choosing between Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol), with D3 often being more effective in raising blood levels of Vitamin D. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and to avoid potential toxicity from excessive intake.
Supplementing with Vitamin D should be done with care, considering factors like age, geographical location, existing health conditions, and current Vitamin D levels. Regular monitoring through blood tests can help adjust the dosage as needed to maintain optimal levels. Additionally, combining Vitamin D supplementation with calcium intake can enhance bone health, particularly in older adults. Misconceptions about supplement safety and efficacy are common, so obtaining accurate information and personalized medical advice is crucial.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Vitamin D Levels

Lifestyle choices significantly impact the body’s ability to synthesize and absorb Vitamin D. Regular physical activity, particularly outdoors, can enhance the body’s natural production of Vitamin D through sunlight exposure. Conversely, obesity can decrease the bioavailability of Vitamin D, making it more difficult for the body to maintain adequate levels. Factors like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also impair Vitamin D metabolism and overall health.
Adopting a holistic lifestyle approach can improve Vitamin D status and general well-being. This includes managing body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, limiting alcohol intake, and avoiding tobacco use. Seasonal changes and work environments that limit sun exposure should also be considered, prompting individuals to adjust their outdoor activities and dietary choices accordingly. Addressing these lifestyle factors is essential for maintaining adequate Vitamin D levels and supporting long-term health.
The Connection Between Vitamin D and Overall Health

Maintaining sufficient levels of Vitamin D is crucial for overall health beyond just bone strength and calcium absorption. It plays a significant role in modulating the immune system, reducing the risk of infections and autoimmune diseases. Emerging research also links adequate Vitamin D levels with a lower risk of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, Vitamin D is believed to play a role in mental health, with deficiencies associated with an increased risk of depression and mood disorders.
The systemic impact of Vitamin D on health underscores the importance of a proactive approach to managing its levels. Regular screening for Vitamin D deficiency, particularly in high-risk groups, can lead to early intervention and prevent a range of health issues. Public health initiatives often emphasize the importance of Vitamin D in disease prevention, advocating for a combination of natural sunlight exposure, dietary intake, and supplementation as needed. Understanding the holistic benefits of Vitamin D can motivate individuals to prioritize their Vitamin D status as part of their overall health strategy.
Monitoring and Maintaining Healthy Vitamin D Levels
Regular monitoring of Vitamin D levels is essential to ensure they remain within a healthy range, especially for those at risk of deficiency. Blood tests can accurately measure serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, the precursor form of the vitamin that reflects overall body stores. Healthcare professionals can use these results to recommend appropriate sun exposure, dietary adjustments, or supplementation. This proactive approach helps in maintaining consistent Vitamin D levels and preventing the oscillation between deficiency and sufficiency.
Maintaining healthy Vitamin D levels requires a long-term commitment to a balanced lifestyle, including adequate sun exposure, a nutritious diet, and regular physical activity. Seasonal variations, particularly in regions with less sunlight during certain times of the year, necessitate adjustments in lifestyle and possibly supplementation to compensate for reduced sun exposure. Educating individuals on the importance of Vitamin D and how to maintain optimal levels is crucial, as it empowers them to make informed health decisions and potentially reduce the risk of associated health complications.
Addressing Challenges and Misconceptions
Overcoming Vitamin D deficiency naturally involves addressing various challenges and misconceptions that can hinder effective management. One common challenge is the misunderstanding of sun exposure needs, with many believing that minimal sunlight is sufficient or, conversely, that excessive sun exposure is without risks. Educating on the balanced approach to sunlight—enough to produce Vitamin D but not so much as to risk skin damage—is crucial. Additionally, the misconception that only outdoor activities contribute to Vitamin D synthesis overlooks the potential of dietary sources and supplements to boost levels.
Misconceptions about Vitamin D supplementation, such as fears of toxicity or doubts about its efficacy, often prevent individuals from achieving optimal levels. Clearing up these misconceptions with factual information and guidance from healthcare professionals can help individuals make better-informed decisions. Addressing the challenge of dietary restrictions or preferences that limit Vitamin D intake, such as veganism or lactose intolerance, is also essential. Providing practical strategies and alternatives, like fortified foods or specific supplements, can aid in overcoming these dietary hurdles and ensure a sufficient intake of Vitamin D.
Embracing the Sunshine Vitamin for Optimal Health
To overcome Vitamin D deficiency naturally, an integrated approach combining safe sun exposure, a nutrient-rich diet, and lifestyle adjustments is essential. Understanding the crucial role of Vitamin D in overall health, from bone strength to immune function, highlights the importance of maintaining adequate levels. Regular monitoring, along with addressing misconceptions and lifestyle factors, can ensure effective management of Vitamin D status. Embracing these strategies empowers individuals to enhance their health proactively, showcasing the undeniable significance of the “sunshine vitamin” in sustaining well-being and vitality.