Obesity has become a pressing issue in modern society, affecting millions of people worldwide. Its prevalence has led to a surge in related health conditions, making it a matter of public health concern. While many view obesity as a cosmetic problem, the reality is far graver. This post explores the various health conditions commonly associated with obesity. From cardiovascular diseases to mental health implications, understanding these risks is the first step toward proactive health management. Let’s explore how obesity is more than just a number on the scale; it’s a condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
Contents
What Is Obesity And How Is It Measured?

Obesity is a medical condition characterized by an excessive amount of body fat. It’s often quantified using metrics like Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference. These measurements serve as useful tools for healthcare providers to assess an individual’s risk for obesity-related health issues. However, it’s essential to note that these are not the only indicators; factors like muscle mass and overall health also play a role.
Various elements contribute to obesity, ranging from lifestyle choices and eating habits to genetic predispositions and environmental factors. For instance, a diet high in processed foods and sugars, coupled with a sedentary lifestyle, can significantly increase the risk of becoming obese. On the other hand, some individuals may be genetically predisposed to obesity, making it crucial to consider a multifaceted approach to diagnosis and treatment.
Cardiovascular Diseases

One of the most alarming health risks associated with obesity is the increased likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases. Conditions such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and elevated cholesterol levels are more common in individuals with obesity. These issues can lead to severe complications, including heart attacks and strokes, making it imperative to manage weight effectively.
Studies have shown a direct correlation between obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Excessive body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can cause inflammation and increase fatty acid levels, impairing the body’s ability to regulate blood pressure and cholesterol. As a result, the heart has to work harder, putting additional strain on the cardiovascular system. This cycle of obesity and heart-related issues underscores the importance of weight management in maintaining heart health.
Type 2 Diabetes
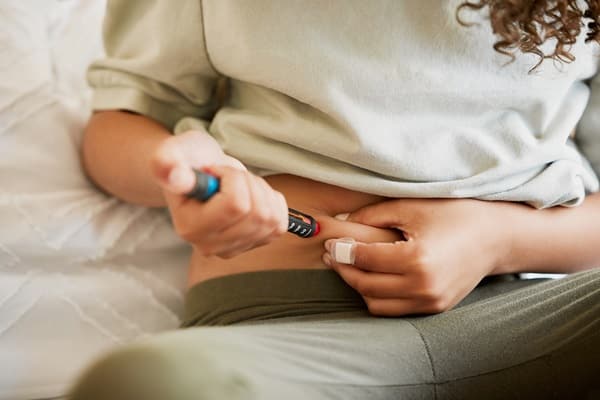

Another significant health condition closely linked to obesity is Type 2 Diabetes. This form of diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Elevated body weight, especially around the abdominal area, is a key factor in the development of insulin resistance, leading to Type 2 Diabetes.
Managing or preventing this condition often involves lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise. Medications may also be prescribed to control blood sugar levels. However, weight loss remains one of the most effective ways to improve insulin sensitivity. By understanding the relationship between obesity and Type 2 Diabetes, individuals can take proactive steps to manage both their weight and blood sugar levels effectively.
Joint And Bone Health
The skeletal system is another area significantly impacted by obesity. Excessive weight places added stress on joints and bones, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis, lower back pain, and even fractures. The knees and hips are particularly vulnerable, as they bear the brunt of the body’s weight, making mobility a challenge for individuals with obesity.
Weight management plays a crucial role in alleviating these joint and bone issues. Studies have shown that even a modest reduction in weight can result in significant improvements in joint pain and function. Exercise, although challenging for those with joint issues, can be tailored to individual needs and can contribute to both weight loss and improved joint health.
Respiratory Problems
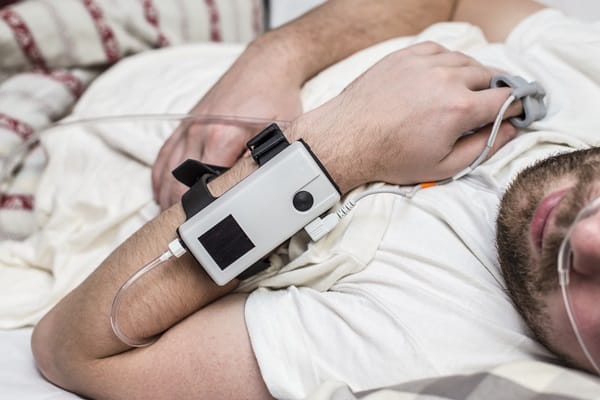

Obesity doesn’t just affect the heart and bones; it also has a profound impact on the respiratory system. Conditions like sleep apnea and asthma are more prevalent among individuals with obesity. Excessive fat around the neck and chest areas can restrict airways, making it difficult to breathe, especially during sleep.
Losing weight can dramatically improve respiratory conditions. For instance, weight loss has been shown to reduce the severity of sleep apnea and may even eliminate the need for treatment in some cases. Similarly, better weight management can lead to improved lung function, making it easier to breathe and reducing the severity of asthma symptoms.
Mental Health Implications
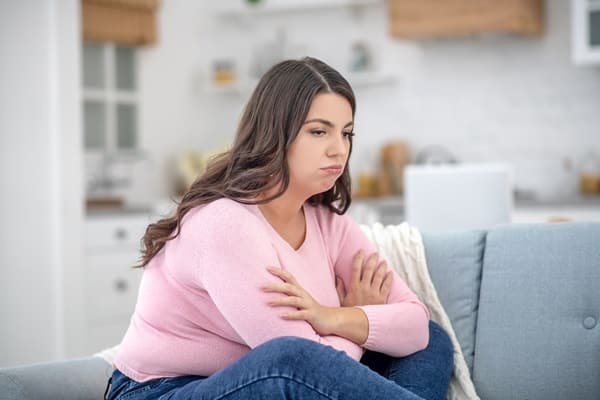

The psychological toll of obesity is often overlooked but is no less significant. Conditions like depression and anxiety are more common among individuals with obesity. The social stigma and discrimination they face can exacerbate these mental health conditions, making it a vicious cycle that is hard to break.
Mental health support and counseling are essential components of treating obesity. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of psychological support can help individuals address the emotional and behavioral aspects of obesity. These treatments often go hand-in-hand with physical interventions, offering a holistic approach to managing both weight and mental well-being.
Reduced Life Expectancy

Perhaps one of the most sobering aspects of obesity is its impact on life expectancy. Studies have consistently shown that obesity is linked to a shorter lifespan due to the cumulative effect of various health conditions like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and even certain types of cancer. The risk of premature death is significantly higher among individuals with obesity.
Early intervention and treatment are crucial in mitigating these risks. Healthcare providers often recommend a multi-pronged approach, including lifestyle changes, medication, and, in some cases, surgical interventions like bariatric surgery. The goal is not just to reduce body weight but to improve overall health, thereby increasing the chances of a longer, healthier life.
Management And Treatment Options

When it comes to managing obesity, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Treatment often involves a combination of diet, exercise, and medication. Healthcare providers usually tailor treatment plans to individual needs, taking into account other existing health conditions. For some, bariatric surgery may be recommended as a last resort when other methods have failed to produce significant weight loss.
Success stories and case studies serve as powerful motivators for those embarking on their weight loss journey. These real-life examples illustrate that with the proper support and resources, it is possible to manage obesity effectively. The key lies in a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of this complex condition.
Take Steps To Address Obesity
In a world where obesity is increasingly prevalent, understanding its associated health risks is more crucial than ever. This article has shed light on how obesity affects various aspects of health, from cardiovascular diseases to mental well-being. The aim is not to stigmatize but to inform and encourage proactive steps toward better health. Consult healthcare providers for personalized advice and take the first step in managing obesity today.