Food poisoning, an unpleasant and potentially dangerous experience, occurs when individuals consume foods contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, or toxins. The effects range from mild discomfort to severe health complications, underscoring the importance of understanding and practicing food safety. This article aims to guide readers through essential rules and practices to minimize the risk of food poisoning. It covers topics from selecting safe ingredients to proper cooking techniques and handling leftovers, offering practical advice for everyday situations. Whether dining at home or eating out, these guidelines will help ensure that meals are delicious and safe to consume, protecting one’s health and that of their loved ones.
Contents
Understanding Food Poisoning

Food poisoning is caused by consuming contaminated foods, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms can appear within hours or even days after eating the tainted food. Food can become contaminated during production, processing, or cooking. Common culprits include bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, viruses like norovirus, and various toxins. While most cases are mild and resolve without treatment, certain groups, such as young children, pregnant women, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems, are at higher risk of severe complications.
Understanding the various pathogens that cause food poisoning and their sources is crucial in prevention. Bacteria thrive in certain conditions, particularly in protein-rich foods at warm temperatures. Viruses, on the other hand, are often transmitted through contaminated water or by infected food handlers. Awareness of these factors is pivotal in adopting safe food handling practices, significantly reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Choosing Safe Ingredients

Selecting safe and high-quality ingredients is the first step in preventing food poisoning. Freshness is key in fruits, vegetables, meats, and dairy products. For produce, look for items free from bruises or damage, where bacteria can thrive. When choosing meat and poultry, ensure they are refrigerated properly and are within their use-by dates. For dairy products, pasteurization is crucial as it kills harmful bacteria.
When shopping, one should also be mindful of their food source. Locally sourced and organic foods can reduce the risk of exposure to certain pesticides and chemicals, though they are not immune to contamination. Ensuring these ingredients are fresh and safe is vital for healthy cooking at home. This enhances the dishes’ flavor and ensures the safety and well-being of those who consume them.
The Importance of Proper Food Storage

Proper food storage is essential to prevent the growth of bacteria that can lead to food poisoning. Different foods require different storage conditions to maintain their safety and quality. Refrigerating perishable items promptly at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) slows down the growth of harmful bacteria. It’s also important to keep raw meat, poultry, and seafood separate from other foods to avoid cross-contamination.
When organizing a refrigerator, raw meats should be stored at the bottom to prevent their juices from dripping onto other foods. Leftovers should be refrigerated within two hours of cooking and consumed within three to four days. Proper food storage extends the life of food items, reduces waste, and, most importantly, protects against foodborne illnesses. By adhering to these simple guidelines, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of encountering food-related health issues.
Safe Food Preparation Practices
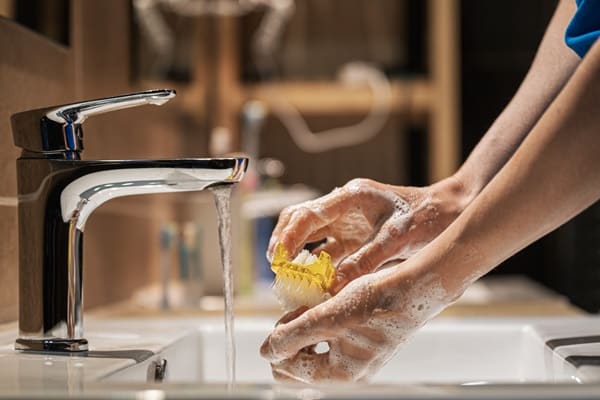

Ensuring cleanliness is the cornerstone of safe food preparation. This involves washing hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling food, especially raw meat, poultry, and seafood. Kitchen surfaces, cutting boards, and utensils should also be cleaned regularly to prevent cross-contamination.
Washing fruits and vegetables under running water before eating or cooking them helps remove dirt, bacteria, or residual pesticides. However, items like poultry and meat should not be washed as this can spread bacteria to other surfaces. By adopting these safe preparation practices, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of contaminating their food and protect themselves and others from food poisoning.
Cooking Food to Safe Temperatures
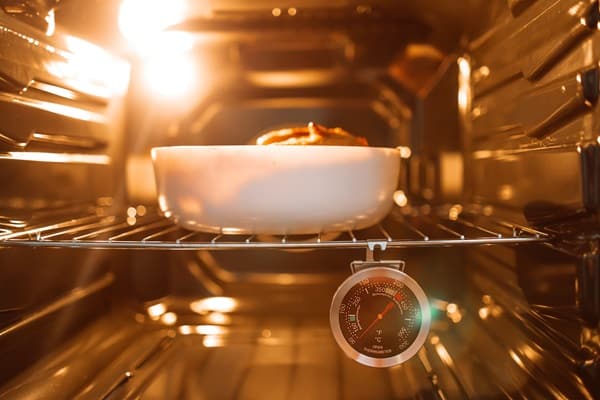

Cooking food to the right temperature is crucial for killing harmful bacteria. The safe internal temperature varies for different types of meat: poultry should reach 160°F and most other meats at 145°F with a resting time of 3 minutes. A food thermometer is the best way to ensure these temperatures are reached, as judging by color or texture can be misleading.
Vegetables and other side dishes must also be cooked properly, especially those in contact with raw meat or its juices. While cooking destroys most bacteria, keeping food at a safe temperature until it is eaten is equally important. Hot foods should remain above 140°F, and cold foods should be kept at or below 40°F to prevent bacterial growth.
Handling Leftovers Correctly
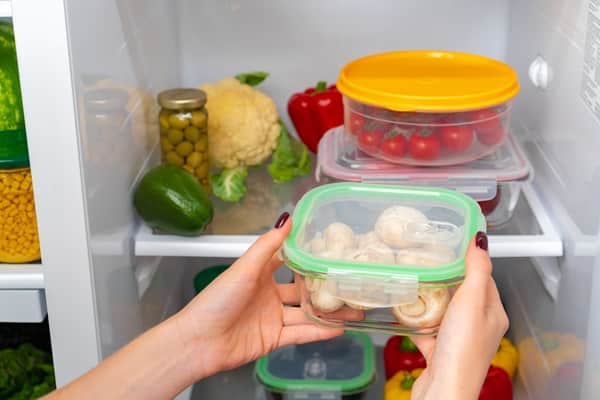

Leftovers can be convenient and economical, but they must be handled properly to avoid food poisoning. They should be cooled quickly and refrigerated within two hours of cooking. When reheating, ensure that the food reaches an internal temperature of 165°F to kill any bacteria that may have grown.
Leftovers should typically be consumed within three to four days, although this can vary depending on the type of food. If there is any doubt about the safety of a leftover item, it is better to err on the side of caution and discard it. This practice ensures safety and helps inculcate a habit of responsible food consumption and waste management.
Dining Out Safely

When dining out, the cleanliness of a restaurant is a key indicator of food safety. Observing whether staff members follow basic hygiene practices, such as wearing gloves or washing hands, can provide insights into the establishment’s overall cleanliness. It is also prudent to check reviews and ratings, offering valuable information about a restaurant’s food handling practices.
For individuals with food allergies or sensitivities, communicating their dietary needs clearly to restaurant staff is essential. Many restaurants now offer allergy-friendly menus or are willing to accommodate special requests, ensuring a safe and enjoyable dining experience for all patrons.
Food Safety for High-Risk Groups
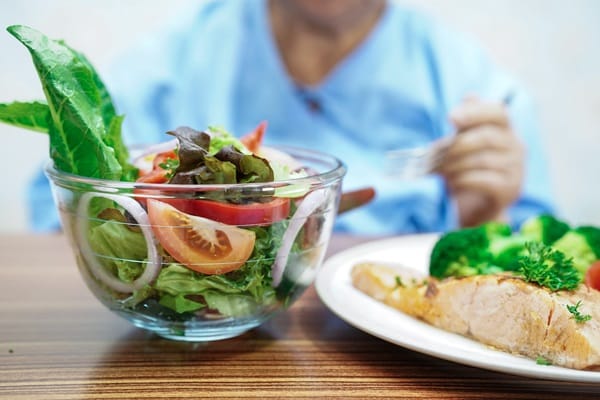

Certain groups, including pregnant women, young children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems, need to take extra precautions with food safety. These individuals are more susceptible to the effects of foodborne illnesses and may experience more severe symptoms.
For these high-risk groups, avoiding certain high-risk foods like unpasteurized dairy products, raw or undercooked meats and seafood, and certain types of fish with high mercury levels is especially important. Special attention should also be paid to food preparation and storage practices to minimize the risk of exposure to harmful pathogens.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, food safety is essential for preventing food poisoning, ranging from mildly uncomfortable to severely hazardous. Individuals can greatly reduce their risk by understanding the causes of food poisoning, choosing safe ingredients, ensuring proper storage and preparation, cooking to the right temperatures, and handling leftovers correctly. These practices are particularly crucial for high-risk groups, who are more vulnerable to the effects of foodborne illnesses. Additionally, being vigilant about food safety when dining out is equally important. Adopting these simple yet effective habits can lead to a healthier lifestyle, providing peace of mind that the food consumed is not only delicious but safe. As the saying goes, prevention is better than cure, especially regarding food safety.