A balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients, is a cornerstone of good health. However, even the most thoughtfully planned diets can sometimes miss key elements, resulting in various health issues. One such element, often overlooked, is iodine. Known for its significant role in thyroid function and metabolic regulation, iodine’s importance extends to various bodily processes. Though seemingly insignificant, a deficiency in this essential mineral can lead to a range of health complications, emphasizing the necessity of adequate consumption. This post aims to uncover the multifaceted role of iodine, exploring its importance, sources, benefits, and risks.
Contents
Understanding Iodine

Iodine, a trace element found in certain foods and supplements, is vital for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. These hormones play a pivotal role in metabolic activities, ensuring that the body utilizes energy efficiently. Iodine’s presence in the human body, though minimal, has a direct impact on physical growth and neurological development. It is a catalyst in the production of thyroid hormones, which are instrumental in processes ranging from cellular regeneration to the metabolic rate. The right amount of iodine ensures a balanced and functional metabolism, acting as a linchpin in overall well-being.
The recommended daily intake of iodine varies among individuals, influenced by factors like age, sex, and health conditions. Babies, children, and pregnant women, for instance, have distinct iodine needs essential for growth and development. Understanding these variances is crucial in avoiding both deficiency and excess. Diverse food sources and supplements can provide the necessary iodine intake, mitigating the risks associated with its inadequacy. By identifying the appropriate daily iodine requirement, individuals can make informed dietary choices to maintain optimal health.
The Role Of Iodine In Thyroid Health
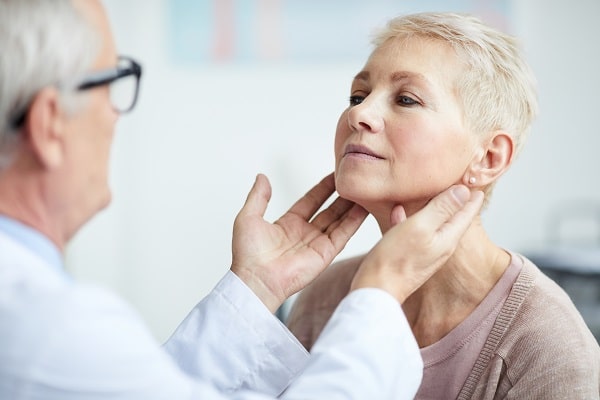
Iodine’s most notable contribution to health is its fundamental role in thyroid function. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is responsible for producing hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism. These hormones, namely thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are synthesized when iodine intake is adequate. A well-functioning thyroid not only ensures energy efficiency but also supports various physiological processes, such as temperature regulation and the maintenance of skin, hair, and nail health.
However, an imbalance in iodine levels can lead to thyroid-related health issues. A deficiency might result in hypothyroidism, characterized by weight gain, fatigue, and sensitivity to cold. On the flip side, an excess of iodine can induce hyperthyroidism, leading to weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and heat sensitivity. Striking a balance in iodine consumption is paramount to evade these health issues and uphold the thyroid’s optimal functioning. Proper education and awareness about the sources and effects of iodine can act as a precursor to a health-conscious society.
Cognitive Function And Development
Iodine plays a crucial role in brain health, especially during the early stages of development. An adequate intake of this mineral is essential for pregnant women, as it influences the neurological growth of the fetus. Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can lead to developmental issues, lower IQ, and in severe cases, cretinism. Neurological growth and cognitive function in children are also heavily dependent on iodine. The mineral aids in the optimal development of motor skills, memory, and attention span, establishing its necessity from the prenatal stage through adolescence.
In adults, sufficient iodine levels contribute to maintained cognitive functions. A deficiency can lead to decreased mental alertness, lowered cognitive abilities, and in some cases, mental retardation. It’s not uncommon for issues like memory loss and reduced intellectual capacity to be linked to low levels of iodine. Addressing this deficiency can improve mental clarity, concentration, and information retention. The correlation between iodine and cognitive health underscores the importance of consistent and adequate intake throughout the lifespan.
Iodine And Immune System

Iodine’s role in bolstering the immune system is another testament to its multifaceted benefits. This mineral enhances the activity of antioxidants in the body, reducing damage caused by free radicals and supporting cellular health. Iodine also promotes the detoxification process, aiding in the elimination of toxins and foreign substances. A strengthened immune system is often the first line of defense against common illnesses and infections, making iodine an essential component of preventative healthcare.
Furthermore, iodine supports the lymphatic system and fosters the production of white blood cells. The element’s antimicrobial properties play a vital role in preventing and fighting infections. Adequate iodine levels ensure that the immune system operates at its peak, minimizing the risk of diseases. Given the rising concerns about antibiotic resistance and emerging pathogens, the role of natural elements like iodine in enhancing immunity has become increasingly significant.
Iodine’s Role In Detoxification

The body’s detoxification process is enhanced by adequate iodine intake. Iodine assists in flushing out chemical toxins, heavy metals, and biological toxins from the body. This is particularly significant in today’s world, where exposure to various environmental pollutants is almost inevitable. By promoting the efficient elimination of these harmful substances, iodine supports overall cellular health and reduces the risk of chronic diseases linked to toxicity.
Iodine also helps mitigate the effects of radiation exposure. In the event of radiation exposure, such as during medical treatments or environmental contamination, iodine can protect the thyroid and other organs from radiation-induced damage. It acts as a shield, reducing the absorption of radioactive iodine isotopes. Thus, in addition to its role in regular detoxification, iodine serves as an essential protective agent against radiation, underscoring its comprehensive health benefits.
Dietary Sources Of Iodine
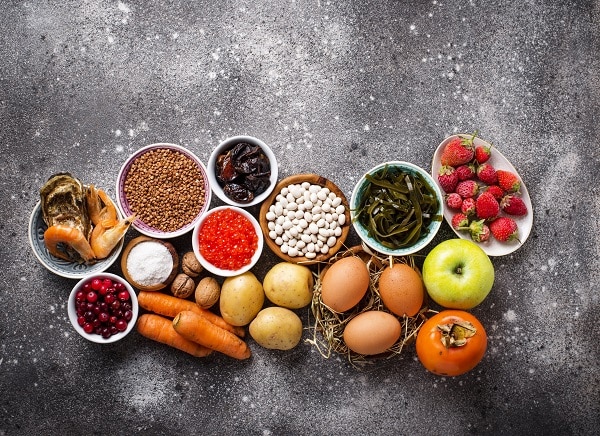

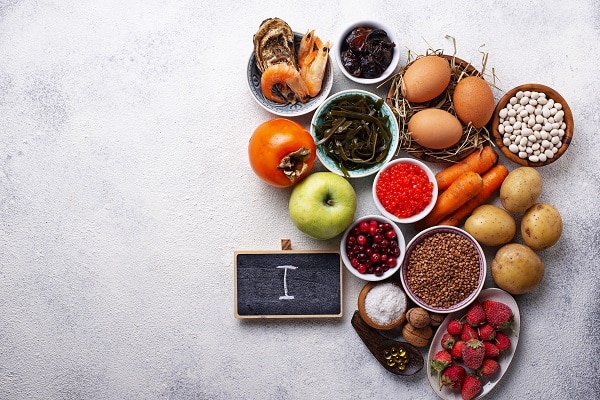
A variety of foods provide a rich source of iodine, essential for maintaining optimal health. Seafood, particularly fish and seaweed, is known to be abundant in this mineral. Incorporating these into the diet can significantly enhance iodine levels, supporting thyroid function and cognitive health. Additionally, dairy products, eggs, and some bread are fortified with iodine, offering an accessible source for those with diverse dietary preferences. It’s essential to explore these options to ensure a balanced intake of iodine, enhancing overall well-being.
For individuals who find it challenging to obtain iodine from natural food sources, supplements can serve as a viable alternative. These are especially beneficial for people with specific dietary restrictions or those living in regions where iodine-rich foods are scarce. However, it’s paramount to approach supplementation with caution, considering the appropriate dosages and potential interactions with other nutrients or medications. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice is always recommended to ensure safety and efficacy.
Risks Associated With Excessive Iodine

While iodine is undeniably essential for various bodily functions, an excessive intake can lead to adverse effects. Hyperthyroidism, characterized by an overactive thyroid, can manifest due to an excess of iodine. Symptoms may include anxiety, insomnia, rapid heartbeat, and weight loss. On a cellular level, too much iodine can lead to oxidative stress, cellular damage, and in severe cases, thyroid cancer. Moderation and balance are key to harnessing the benefits of iodine without the associated risks.
Conversely, iodine deficiency, marked by an underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism, is also a concern. However, the focus should be on achieving a balanced intake rather than an excessive one. Strategies to achieve this balance include diversifying dietary sources of iodine, being mindful of the consumption of iodine-rich foods and supplements, and seeking professional medical advice for individualized recommendations. Awareness and education about the dual risk of deficiency and excess can facilitate informed decisions that promote health and well-being.
The Bottom Line
The pivotal role of iodine in health and well-being is underscored by its myriad contributions to thyroid function, cognitive development, immune system bolstering, and detoxification. Navigating the fine balance to avoid both deficiency and excess is paramount for optimal health. Dietary diversification, informed supplementation, and awareness of iodine’s comprehensive impacts can foster a holistic approach to health. Individuals are encouraged to explore, understand, and apply this knowledge, positioning iodine as a vital component in the journey to optimal well-being while always considering personal health statuses and needs.