Vegetables play a pivotal role in a balanced and healthy diet, offering a plethora of nutrients essential for maintaining optimal health. The cooking method chosen can significantly impact the nutritional value and taste of these vital foods. This blog post explores various cooking techniques, emphasizing how each method can preserve or enhance the nutritional quality and flavor of vegetables. From steaming to roasting, each approach offers unique benefits, making it important to understand their effects to make informed choices that align with health goals and personal preferences.
Contents
Steaming Vegetables
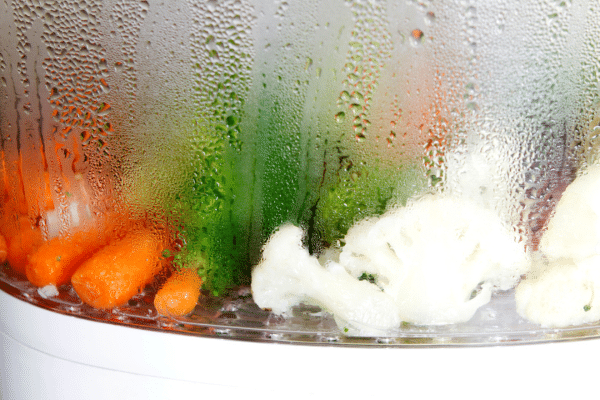
Steaming stands out as one of the most health-conscious methods for cooking vegetables. This technique preserves vital nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, which are often lost during other cooking processes. The gentle heat of steam cooks vegetables thoroughly without necessitating the addition of oils or fats, making it an ideal choice for those monitoring their calorie intake. Furthermore, steaming maintains the natural texture and color of vegetables, enhancing their appeal on the plate. It’s particularly effective for cooking delicate vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and asparagus, which can easily lose their vibrant colors and crisp textures when overcooked.
This method isn’t just beneficial for health; it’s also remarkably convenient and versatile. With the right equipment, such as a steamer basket or an electric steamer, vegetables can be cooked in a matter of minutes. The simplicity of steaming allows the natural flavors of vegetables to shine, reducing the need for heavy seasonings or sauces. Moreover, it’s a great way to prepare multiple vegetables simultaneously, saving time and effort. Steaming is also ideal for those on a sodium-restricted diet, as it requires no additional salt or high-sodium seasonings.
Roasting Vegetables
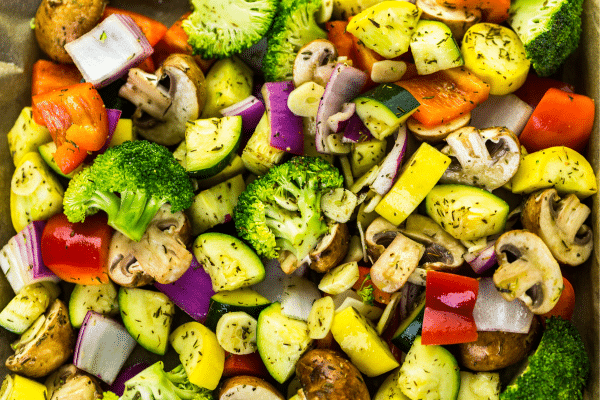
Roasting is a method that uniquely transforms the flavors of vegetables. When vegetables are roasted, the high heat caramelizes their natural sugars, resulting in a rich, sweet, and often smoky flavor that’s hard to achieve with other cooking methods. This process not only brings out an impressive depth of flavor but also provides a satisfying texture, with a crispy exterior and tender interior. Root vegetables like carrots, potatoes, and beets especially benefit from roasting, as their flavors deepen and intensify, appealing to even the pickiest of eaters.
In addition to its flavor-enhancing properties, roasting is surprisingly healthful when done correctly. By using a light coating of a healthy oil, such as olive or avocado oil, it’s possible to achieve the desirable crispy texture without overloading on unhealthy fats. The key lies in the balance – enough oil to facilitate cooking and flavor, but not so much that it detracts from the vegetables’ natural health benefits. To maximize the nutritional value, it’s recommended to roast at moderate temperatures and avoid charring the vegetables, thus preserving more of their essential vitamins and minerals.
Sautéing And Stir-Frying
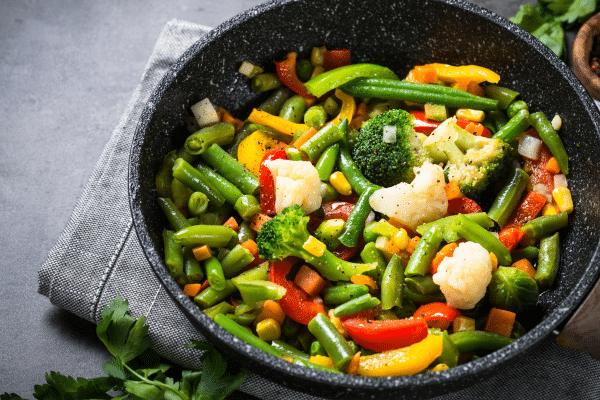

Sautéing and stir-frying are dynamic methods that cook vegetables quickly while maintaining their texture and nutrients. These techniques, often used in a variety of cuisines, require only a small amount of oil and high heat to effectively cook vegetables. The key is to cut the vegetables into uniform pieces for even cooking. Sautéing involves cooking vegetables in a small amount of oil over medium-high heat, allowing them to brown slightly and develop a rich flavor. Stir-frying, on the other hand, is a faster process that involves continuously moving the vegetables around in a wok or frying pan, ensuring that each piece cooks evenly without losing its crunch.
When choosing oils for sautéing or stir-frying, it’s crucial to select those with a high smoke point, such as canola or peanut oil, to withstand the high temperatures without burning. This method not only retains the vitamins and minerals in the vegetables but also incorporates the benefits of healthy fats. Additionally, this technique allows for the inclusion of a variety of vegetables in one dish, making it easy to create a colorful, nutrient-rich meal. The quick cooking time helps retain the bright colors and textures of the vegetables, making the dish visually appealing and nutritionally robust.
Blanching And Shocking
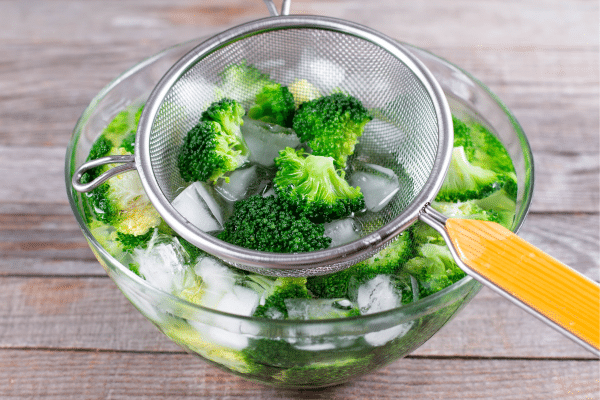

Blanching is a technique that involves briefly boiling vegetables and then rapidly cooling them in ice water, known as shocking. This process is particularly useful for preserving the vibrant color, crisp texture, and nutritional value of vegetables. It’s commonly used for green vegetables like broccoli, green beans, and spinach, which tend to lose their appealing color and texture when overcooked. Blanching also helps in removing any surface dirt and bacteria, making the vegetables safer for consumption. Additionally, this method partially cooks vegetables, making them ready for further cooking or immediate consumption.
The shocking process that follows blanching is crucial for stopping the cooking process, ensuring that vegetables maintain their desired texture. This technique is particularly beneficial when preparing vegetables for salads, crudité platters, or as a pre-cooking step before freezing. It helps in retaining the essential vitamins and minerals often lost during longer cooking processes. Moreover, blanched and shocked vegetables are easier to digest and more palatable, especially for those who prefer a slightly softer texture without compromising the nutritional benefits.
Grilling Vegetables
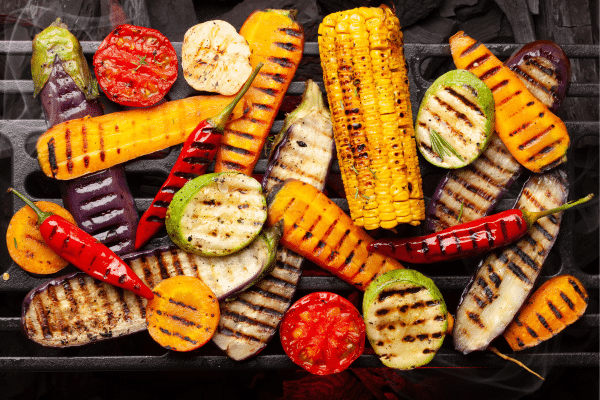
Grilling offers a unique way to cook vegetables, imparting a distinct smoky flavor while preserving their nutritional integrity. This method is ideal for a variety of vegetables, especially those with a firmer texture like zucchini, bell peppers, and corn on the cob. The high heat of the grill chars the vegetables slightly, creating a tantalizing combination of smoky and caramelized flavors. Grilling is also a low-fat cooking method, as it requires minimal oil, making it a healthy choice for those mindful of their fat intake.
To grill vegetables successfully, it’s important to cut them into sizes that will cook evenly and not fall through the grill grates. Lightly coating the vegetables with a healthy oil can prevent sticking and help in achieving a crispy exterior. Using marinades or herbs can also add additional flavor without the need for excess salt or fat. Grilling not only brings a delightful taste to vegetables but also makes for an enjoyable outdoor cooking experience. This method is especially popular in the warmer months, allowing for the preparation of healthy and flavorful vegetable dishes.
Microwaving Vegetables
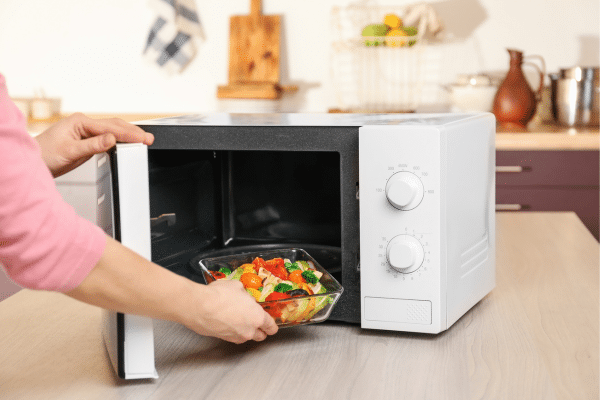

Microwaving is often misunderstood, yet it’s an incredibly efficient and nutritious way to cook vegetables. This method uses less water than traditional boiling, which helps in retaining more vitamins and minerals. Microwaving is also fast and convenient, making it an excellent option for those with limited time. Vegetables cooked in the microwave often retain their color, texture, and flavor, debunking the myth that microwave cooking leads to bland, overcooked food.
To maximize the benefits of microwaving, it’s advisable to use minimal water and cover the vegetables during cooking. This creates a steam environment that cooks the vegetables evenly while preserving their moisture. It’s also important to cut the vegetables into uniform sizes for even cooking. Microwaving is particularly suitable for cooking small quantities of vegetables, making it a practical choice for single servings or small families. Additionally, since microwaves vary in power, it’s crucial to adjust cooking times accordingly to prevent overcooking.
Boiling Vegetables
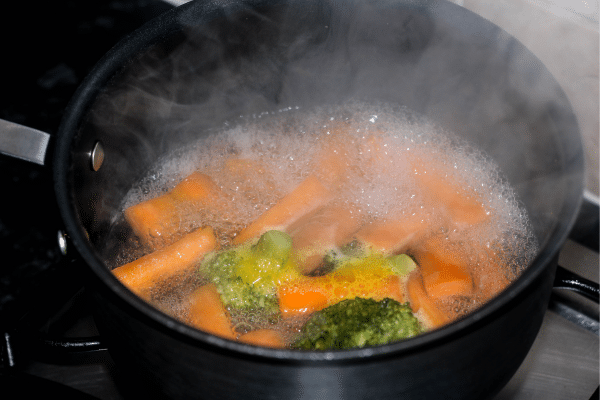

Boiling is one of the most traditional methods for cooking vegetables but requires careful execution to preserve their nutritional value. While boiling is simple and effective, it can lead to the leaching of water-soluble vitamins and minerals into the cooking water. To minimize nutrient loss, it’s advisable to use as little water as possible and to cook the vegetables for the shortest time necessary. This method is particularly effective for denser vegetables like potatoes, carrots, and beets.
Another strategy to reduce nutrient loss is to repurpose the cooking water. For instance, the water used for boiling can be used as a base for soups or sauces, thereby recapturing some of the lost nutrients. Boiling is also beneficial for softening vegetables, making them easier to digest, especially for those with digestive issues. While boiling may not be the most nutrient-preserving method, it can still be a healthy cooking option when done correctly.
The Bottom Line
Each vegetable cooking method offers unique benefits, allowing for a range of flavors, textures, and nutritional qualities. From the nutrient-retaining techniques of steaming and microwaving to the flavor-enhancing qualities of roasting and grilling, there’s a method suited to every taste and health requirement. The key is to understand the characteristics of each technique and to choose the one that aligns best with the desired outcome, whether it’s maximizing nutrient retention, achieving a specific texture, or enhancing natural flavors. Balancing these methods in a varied diet ensures a delightful and healthful culinary experience with vegetables.