Air pollution remains a pervasive threat to public health, impacting millions globally. It is not just an environmental issue but a major contributor to a range of health problems. From exacerbating respiratory diseases to influencing the development of chronic conditions, the effects of air pollution are far-reaching and complex. This post delves into the multifaceted ways in which air pollution adversely affects health, highlighting the urgency of addressing this silent killer.
Contents
Cardiovascular Disease
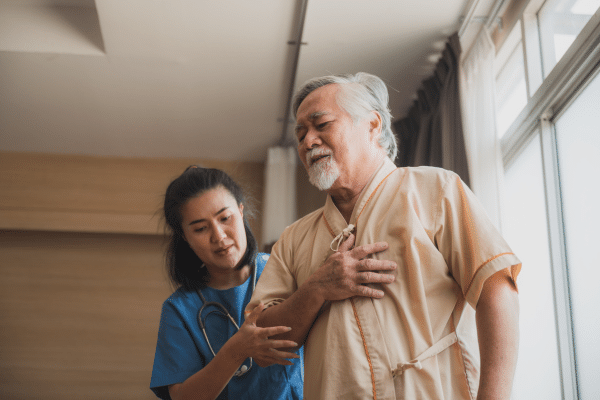

Air pollution significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Particulate matter, one of the primary pollutants, can penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, causing inflammation and oxidative stress. This leads to arterial plaque formation, a key factor in heart attacks and strokes. Long-term exposure to air pollutants has been linked to elevated blood pressure, arrhythmias, and other heart-related complications. Studies suggest that even short-term exposure at high levels can trigger acute cardiovascular events.
Another aspect of cardiovascular risks involves the lesser-known gaseous pollutants like nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. These gases, often originating from vehicle emissions and industrial processes, contribute to the development of heart diseases. They interact with other atmospheric components to form secondary pollutants, further complicating the health impacts. The association between these pollutants and chronic heart conditions underscores the need for more stringent air quality regulations.
Asthma Attacks

Exposure to air pollution is a well-known trigger for asthma attacks. Pollutants like ozone, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides exacerbate respiratory conditions, leading to increased frequency and severity of asthma symptoms. These airborne irritants cause inflammation and narrowing of airways, making breathing difficult for individuals with asthma. Moreover, high pollution days often see a spike in hospital admissions for asthma-related complications, highlighting the direct impact on sufferers.
Long-term exposure to poor air quality not only triggers asthma attacks but also contributes to the development of asthma in individuals who previously did not have the condition. Children, in particular, are at a higher risk due to their developing respiratory systems and higher breathing rates relative to their body size. Regular exposure to polluted air during childhood can lead to chronic respiratory problems later in life, necessitating improved air quality standards, especially in urban areas.
Cognitive Decline

There is a growing body of evidence linking air pollution to cognitive decline in both adults and children. Exposure to pollutants, particularly fine particulate matter, is associated with reduced cognitive function and an increased risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. These particles can cross the blood-brain barrier, leading to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are detrimental to brain health.
In children, the impact of air pollution on brain development is particularly alarming. Studies have shown that children exposed to high levels of air pollution perform worse on tests of memory, attention, and even IQ. This exposure during critical developmental stages can have long-lasting effects, potentially leading to decreased academic performance and future cognitive challenges. These findings underscore the importance of reducing air pollution levels to protect the most vulnerable populations, especially children.
Aggravation Of Allergies

The correlation between air pollution and the aggravation of allergies is increasingly evident. Pollutants such as particulate matter, ozone, and sulfur dioxide exacerbate allergy symptoms by irritating the respiratory tract. This irritation can lead to increased sneezing, coughing, and nasal congestion in individuals with pre-existing allergies. Furthermore, air pollution can alter the immune response, making the body more sensitive to allergens. This heightened sensitivity can result in more severe allergic reactions and a prolonged allergy season.
Moreover, air pollutants can directly interact with allergens, making them more potent. Pollen, when combined with certain air pollutants, becomes more aggressive, leading to more intense allergic responses. This phenomenon is particularly troubling for urban populations, where high levels of pollution and allergens often coexist. The increasing severity and duration of allergy seasons can be attributed, in part, to rising air pollution levels, emphasizing the need for effective air quality management strategies.
Lung Cancer

Air pollution is a significant risk factor for lung cancer, with numerous studies establishing a clear link. Long-term exposure to pollutants, especially fine particulate matter and carcinogenic substances like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), increases the risk of developing lung cancer. These particles and compounds can cause damage to lung tissue, leading to mutations and cancerous growths over time. The risk is not limited to outdoor air pollution; indoor pollutants, such as radon and secondhand smoke, also contribute significantly to lung cancer risk.
Understanding the mechanisms through which air pollution contributes to lung cancer is crucial for public health strategies. Airborne carcinogens initiate and promote the progression of malignant cells in the lungs. These carcinogens can also suppress the immune response, allowing cancer cells to thrive. The association between air pollution and lung cancer underlines the importance of reducing exposure to both outdoor and indoor air pollutants.
Increased Risk Of Infection
Air pollution compromises the immune system, increasing susceptibility to various infections, particularly respiratory infections. Pollutants such as particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen oxides impair the respiratory tract’s defenses, making it easier for pathogens to enter and infect the body. People living in areas with high levels of air pollution often experience a higher incidence of respiratory infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis. This vulnerability is particularly concerning for children and the elderly, whose immune systems are either developing or weakened.
Additionally, air pollution can exacerbate the severity of infections once contracted. Polluted air can prolong the duration of infections and hinder recovery by continuously irritating the respiratory system and weakening immune responses. The direct relationship between air pollution and increased risk of infections highlights the importance of improving air quality for public health.
Risks During Pregnancy

Pregnancy complications are another serious concern associated with air pollution. Exposure to pollutants during pregnancy is linked to adverse outcomes, such as preterm birth and low birth weight. These complications can have long-term health implications for the child, including developmental delays and chronic health issues later in life. Pregnant individuals exposed to high levels of air pollution face a higher risk of gestational hypertension and diabetes, conditions that can affect both the mother and the fetus.
The effects of prenatal exposure to air pollution extend beyond birth. Studies indicate that children exposed to high levels of pollutants in utero may experience impaired lung development, increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, and even cognitive and behavioral issues. These findings underscore the critical need for pregnant individuals to be aware of air quality and for societies to work towards cleaner air to safeguard the health of future generations.
The Bottom Line
Air pollution is not just an environmental concern but a major public health issue. The impact of polluted air spans from cardiovascular diseases to cognitive decline, exacerbating allergies, increasing the risk of lung cancer, and causing complications during pregnancy. Each of these health issues underscores the urgent need for collective action to improve air quality. Addressing air pollution requires coordinated efforts at both local and global levels, emphasizing the necessity of policy changes, technological advancements, and individual awareness and action. The health of current and future generations depends on the actions taken today to clean the air breathed every day.